Precision over power: How Iran’s ‘obsolete’ missiles penetrated Israel’s air defenses

The Cradle, 19 April, 2024 ─
Iran’s 13 April retaliatory missile strike on Israel, dubbed Operation True Promise, managed to overcome the occupation state’s integrated air defense systems and external foreign support.
The strike, intended to deter future actions by Israel against Iranian personnel and facilities, was notably executed to avoid casualties and serious damage. The operation was especially bold as it targeted Israel, an undeclared nuclear power.
Open-source intelligence from videos and photographs identified multiple warheads striking Ramon airbase in the Negev, not Nevatim, as previously reported, although the occupation army confirmed strikes on Nevatim and released images showing minor damage. This suggests a systematic failure of Israel’s lauded air defenses against those five missiles that hit their target, one after the other.
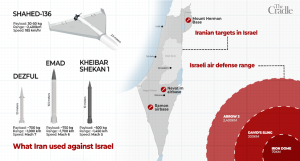
A look at the missiles used
As Brigadier-General Ali Hajizadeh, the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) Aerospace Force’s commander, later stated:
We attacked Israel using obsolete weapons and minimal means. At this stage, we did not use Khorramshahr, Sejjil, Shahid Haj Qassem, Kheibar Shekan[-2], and Hypersonic-2 missiles.
So what missiles did Iran deploy from its significant domestically-produced arsenal, and why?
Ghadr: Despite being 20 years old, this missile proved effective by deploying decoy warheads to exhaust Israel’s Arrow-2 intercept capabilities. While traversing in space, the Ghadr releases about 10 decoy warheads to lure Arrow-2 to launch 10 interceptors each at all 10 Iranian decoys – draining the enemy’s munitions stock.
The images of Israeli interceptors responding to a range of “lights in the skies” were, in fact, often just firing at decoys. The actual Iranian warheads, if not differentiated by Arrow-2’s systems and destroyed by its interceptors, reached their targets.
The missile is still relevant in Iran’s arsenal as it can create additional targets for the enemy’s missile defenses and suppress the operation of large-area assets, such as airbases.
Dezful: A compact, cost-effective missile with a 600 to 700-kilogram payload, apparently used specifically to strike at an Israeli intelligence base in the occupied northern Golan, demonstrating its strategic deployment within its range limits.
This is a low-cost, single-stage precision missile weighing just about 6 tons, yet able to reach Israel – a revolutionary advancement for Iran when Dezful entered service five years ago – but not Nevatim, because its range is about 1,000 kilometers.
Emad: Approximately a decade old, this was used to test Iran’s countermeasures against newer air defense systems like Israel’s Arrow-3 and the American SM-3. It releases inflatable decoys in space to evade interception before re-entry.
Kheibar-Shekan-1: (early model, not the Kheibar-Shekan-2): IRGC’s answer to Israel’s Arrow-3. Kheibar-Shekan-1 entered service with IRGC Aerospace Force in 2022. It counters Arrow-3 by flying on a “depressed trajectory.”
During the terminal phase of its flight, the Kheibar-Shekan-1 performs aerodynamic maneuvers designed to evade interception from multiple defense systems, including Arrow, Patriot, and David’s Sling.
These maneuvers, likened to a boxer dodging punches, complicate the interception process by forcing defense systems to delay their responses or deploy multiple interceptors, reducing their overall effectiveness.
The Kheibar-Shekan-1 forces missile defenses to launch in the “launch-on-remote” mode, meaning several interceptors are required against a single missile. The successful strikes attributed to this missile, as indicated by Israel – with nine confirmed hits – underline its effectiveness and represent a significant evolution in missile technology despite being a generation behind the most recent IRGC models.
Kheibar-Shekan-1’s maneuverability makes it the most likely candidate to have achieved the successful strikes captured by video imagery.
Iranian media has since quoted Hajizadeh saying, “At this stage, we did not use the Khorramshahr, Sejjil, Shahid Haj Qassem, Kheibar-Shekan[-2], and Hypersonic-2 missiles,” which are all part of Iran’s advanced missile arsenal. That does not necessarily preclude Iran’s use of the older Kheibar-Shekan-1 missile, which still appears to be the most likely Iranian missile used to achieve direct hits successively.
‘Weaker than a spider’s web’
Despite Israel’s integrated air defense system, which is bolstered by data from a US monitoring station in the Negev Desert and 36-hour prior notification of the strike from Tehran, multiple Iranian missiles successfully struck their targets.
The US station monitors Iranian missile launches, with the collected data intended to enhance Israel’s defensive response. But despite the support of a multi-nation coalition, which included Jordan defending its airspace and Saudi Arabia and the UAE providing intelligence, Israel’s defenses were breached.
While Israel engaged in GPS jamming before the Iranian attack, its efforts proved futile. Such “electronic warfare” measures cannot counter Iran’s ballistic missiles. Although older drone models are susceptible to this, Iran’s Shahed-136 drone models have been “hardened” against GPS jamming.
This is likely based on Russian experiences in the Ukrainian military theater that were shared with the IRGC Aerospace Force. IRGC’s missiles use “inertial guidance systems,” which rely on built-in guidance systems like gyroscopes and computers.
An inertial guidance system receives input at and just after launch. At this point, it ceases to receive data from the IRGC launch base and relies solely on its onboard systems. That the missiles traveled 1,000 to 1,200 kilometers and struck targets with pinpoint accuracy guided solely by onboard systems is a superlative achievement by Iran.
Israel’s defense credibility at stake
Israel and its allies claim hundreds of missiles and drones were launched by Iran. However, estimates favorable to the Iranian side suggest only 50 to 60 missiles were launched, with 9 to 15 striking their designated targets.
The Israeli military’s propagandist claim of a 99 percent interception rate would fall to about 50 or 60 percent if the above estimate is accurate. The Israeli claim on the number of missiles may be inflated if they are counting the decoys deployed by Ghadr missiles. If so, the picture would look much grimmer for Israel’s missile defense performance.
Hence, to save face and contain escalation, a politically driven inflation of overall launches is evident. This is in line with US interests, which seek to prevent escalation by Israel. Whether Washington’s aim of containing the crisis would allow it to publish the true number is unclear, particularly if the Iranian salvo was small. If it were proven that a relatively small Iranian salvo managed to defeat a complex missile defense system, Israel would lose its aura of invincibility.
Sending a clear message
The types and quantities of missiles Iran chose to use in this strike are not just military tactics but also political messages intended to demonstrate capabilities and expose vulnerabilities in Israel’s air defense systems.
What is evident, though, is that once multiple Iranian warheads penetrate Israel’s air defense systems and strike critical targets, an equation-changing political-military event has occurred. This is to say, Iran made a powerful statement by breaking through Israel’s air defenses and doing so with older ballistic missiles.
In response to threats from Israel about targeting Iran’s uranium enrichment facilities, the resilience of Iran’s nuclear infrastructure poses a significant challenge to the occupation state’s conventional capabilities.
Despite the drawbacks, the potential political gains from such an attack might be considered favorable by embattled Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and his right-wing, nationalist government.
In contrast, Iran’s response to any Israeli attack on nuclear facilities like Natanz or Fordow would likely be intense, drawing on the full capabilities of the IRGC Aerospace Force. It would also – to the horror of Tel Aviv and Washington – potentially lead to a revision of the Islamic Republic’s nuclear doctrine – as was suggested on 18 April by Iran’s Nuclear Centers Protection and Security Corps, Brigadier General Ahmed Haq Talab.
